This article covers the following sections in the KADCYLA Prescribing Information: Section 11 (Description), Section 12 (Clinical Pharmacology), and Section 13 (Nonclinical Toxicology).
11. Description
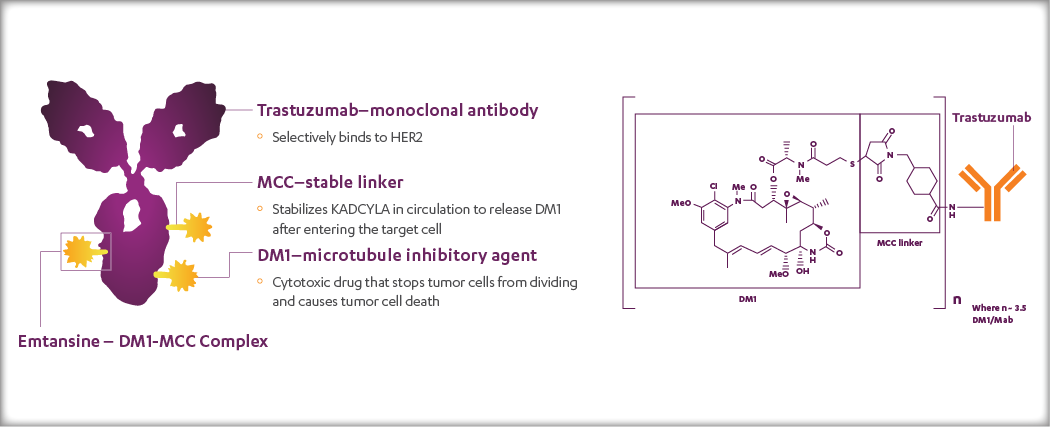
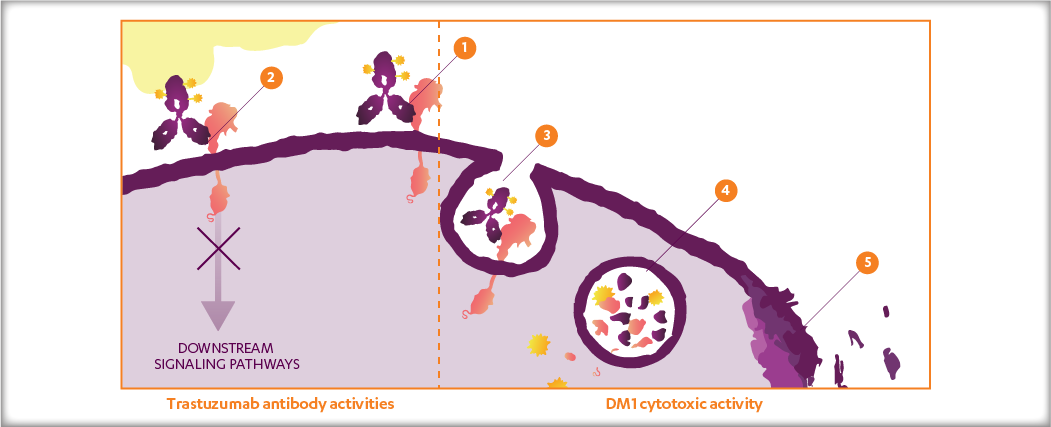
KADCYLA (ado-trastuzumab emtansine), which may also be referred to as T-DM1, is a HER2-targeted antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) which contains the humanized anti-HER2 IgG1, trastuzumab, covalently linked to the microtubule inhibitory drug DM1 (a maytansine derivative) via the stable linker MCC. Emtansine refers to the DM1-MCC complex.
The chemical structure of KADCYLA and an accompanying schematic are shown in the figure below.
KADCYLA: A HER-2-Targeted ADC